AppSealing provides Data Sealing that encrypts and protects sensitive data files. To use Data Sealing, you must follow the file naming convention below. Currently, Data Sealing only supports Native File I/O functions.
📌 Data Sealing File Naming Convention

The Data Sealing file naming convention is simple. If the file name starts with the ' asdp_ ' keyword, the file is recognized as a data sealing file. After sealing, encryption/decryption is automatically applied in the process of writing and reading this data as shown below. (res is applied only in res/raw directory)
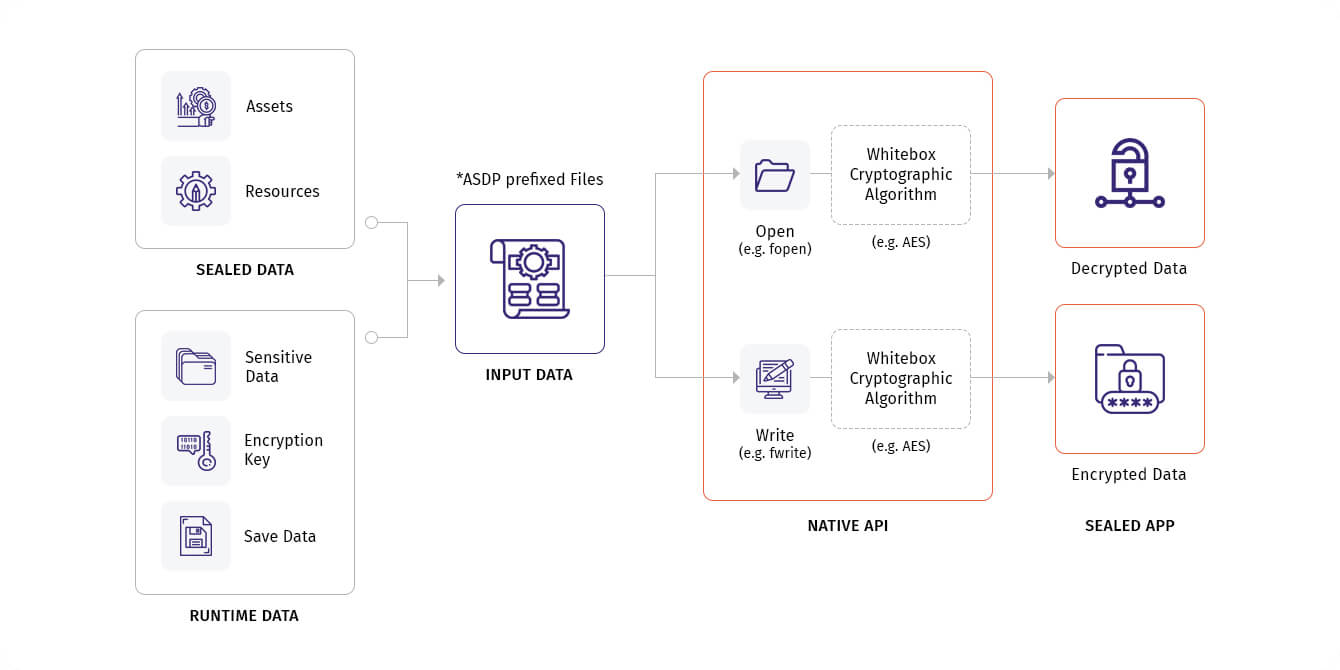
📌 Native File I/O Support
Data Sealing currently supports only Native File I/O functions. Therefore, in an environment developed with Java/Kotlin, the file input/output part must be converted to the NDK (C/C++) environment. The following Native File I/O functions are supported:
- Supports fopen File I/O functions
fopen
fseek
ftell
fread
fwrite
fclose- Supports AAsset functions
AAssetManager_open
AAsset_getBuffer
AAsset_getLength
AAsset_getLength64
AAsset_getRemainingLength
AAsset_getRemainingLength64
AAsset_read
AAsset_seek
AAsset_seek64
AAsset_close
📌 Basic example of converting Java to Native C/C++
Example of reading a Native File I/O file
- Java (Does not support Data Sealing)
/**
* Read a file using FileInputStream
*
* @param filePath (ex) asdp_sample.txt
* @return
*/
public String getFileText(String filePath) {
String dataText = "";
FileInputStream fileStream = null;
try {
fileStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
byte[] buffer = new byte[fileStream.available()];
int count = fileStream.read(buffer);
if (count > 0) {
dataText = new String(buffer, 0, count);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
fileStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return dataText;
}- NDK (C/C++)
/**
* Read a file using fopen
*
* @param env jni function default parameter
* @param cls jni function default parameter
* @param filePath (ex) asdp_sample.txt
* @return
*/
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_appsealing_datasealing_test_TestNative_getFileText(JNIEnv* env,
jobject cls,
jstring filePath)
{
const char* testPath = env->GetStringUTFChars(filePath, 0);
FILE * fp = fopen(testPath, "rb");
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars( filePath, testPath );
if(fp == NULL)
{
LOGE("File fopen failed.");
// File open failed
return env->NewStringUTF("");
}
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
int size = ftell(fp); // get file length using ftell
char buffer[10240] = { 0x00, };
int len;
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
len = fread(buffer, size, 1, fp);
LOGD("%s size: %d, len: %d\n", buffer, size, len);
std::string dataText = buffer;
fclose(fp);
return env->NewStringUTF(dataText.c_str());
}
Example of reading a Native AAset file
- Java (Does not support Data Sealing)
/**
* Read a file using Asset Manager
*
* @param assetName (ex) asdp_sample.txt
* @return
*/
public String getAssetFileText(String assetName) {
String assetText = "";
AssetManager assetManager = context.getAssets();
InputStream stream = null;
try {
stream = assetManager.open(assetName);
byte buffer[] = new byte[stream.available()];
if (stream.read(buffer) > 0) {
assetText = new String(buffer);
}
stream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return assetText;
}- NDK (C/C++)
/**
* Read a file using AAssetManager
*
* @param env jni function default parameter
* @param cls jni function default parameter
* @param assetManager (ex) java:context.getAssets()
* @param assetName (ex) asdp_sample.txt
* @return
*/
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_appsealing_datasealing_test_TestNative_getAssetFileText(
JNIEnv* env,
jobject cls,
jobject assetManager,
jstring assetName) {
const char* temp = env->GetStringUTFChars(assetName, 0);
std::string asset_name = temp;
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars( assetName, temp );
AAssetManager* am = AAssetManager_fromJava(env, assetManager);
AAsset* asset = AAssetManager_open(am, asset_name.c_str(), AASSET_MODE_UNKNOWN);
if (asset == NULL)
return env->NewStringUTF("");
int fileSize = AAsset_getLength(asset);
if (fileSize == 0)
return env->NewStringUTF("");
std::string assetText(fileSize + 1, 0x00);
AAsset_read(asset, (void*)assetText.data(), fileSize);
AAsset_close(asset);
return env->NewStringUTF(assetText.c_str());
}